Examples
This section contains example scripts demonstrating the usage of the Prism API.
Getting Started
from prismapi import Prism
# Initialize the Prism interface
prism = Prism()
# Get available measurement types
print("Available measurements:")
for measurement in prism.get_measurement_types():
print(measurement)
# Move bed to imaging position
prism.move(106, 418)
# Turn on camera light
prism.set_parameter("camera_led_color", 100)
# Capture a bed camera image
image = prism.image_bed()
# Display the captured image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(image)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
# Get parameter information
print("\nAvailable parameters:")
for parameter in prism.get_all_parameters():
print(parameter)
# Move the bed
prism.move(101, 179) # in millimeters
print("\nMoved bed to target position.")
# Set a parameter value
prism.set_parameter("srpl_las_pow_t", 100)
print("\nSet SRPL laser power to 100 uW.")
# Perform a single measurement
measurement = prism.single_measure("srpl")
print(f"\nTook single SRPL measurement.")
print(
f"Measurement routine took {measurement.finish_time - measurement.start_time} seconds."
)
print(f"X data: {measurement.x_data}")
print(f"Y data: {measurement.y_data}")
# Clean up
prism.close()
SRPL Measurement
from prismapi import Prism
prism = Prism()
assert (
"srpl" in prism.get_measurement_keys()
), "SRPL measurement not supported by this device."
print("\nSRPL PARAMETERS:")
for parameter in prism.get_all_parameters():
if "srpl" in parameter.key:
print(parameter)
prism.set_parameter("srpl_las_pow_t", 100, timeout=1)
print("Set laser power to 100 microwatts.")
prism.set_parameter("srpl_integ_time", 0.01, timeout=1)
print("Set integration time to 0.5 seconds.")
measurement = prism.single_measure("srpl")
print(measurement.start_time, measurement.finish_time)
print(f"Measurement took {measurement.finish_time - measurement.start_time} seconds.")
print(f"Wavelength range: {measurement.x_data[0]} - {measurement.x_data[-1]} nanometers")
print(f"Integrated counts: {measurement.y_data.sum()}")
prism.set_parameter("srpl_integ_time", 0.01)
print("Set integration time to 10 milliseconds.")
prism.start_running_measure("srpl")
for i in range(5):
prism.wait_for_new_data("srpl", timeout=1)
measurement = prism.get_last_measurement("srpl")
print(f"Collected running measurement {i}. Integrated counts = {measurement.y_data.sum()}")
prism.stop_running_measure("srpl")
prism.close()
Transient Measurement
from prismapi import Prism
from time import time
prism = Prism()
assert (
"srpl" in prism.get_measurement_keys()
), "SRPL measurement not supported by this device."
print("Moving to sample position.")
prism.move(86, 10)
print("\nSRPL PARAMETERS:")
for parameter in prism.get_all_parameters():
if "srpl" in parameter.key:
print(parameter)
# Set integration time to 10 milliseconds
prism.set_parameter("srpl_integ_time", 0.01)
print("Set integration time to 10 milliseconds.")
# Start continuous measurement
prism.start_running_measure("srpl")
# Set laser to high intensity of 5 milliwatts
prism.set_parameter("srpl_las_pow_t", 5000, timeout=1)
print("Set laser power to 5 milliwatts.")
print("Starting transient measurement...")
start_time = time()
for i in range(100):
prism.wait_for_new_data("srpl", timeout=1)
measurement = prism.get_last_measurement("srpl")
print(f"Collected measurement at {measurement.finish_time - start_time} seconds.")
print(f"Y data: {measurement.y_data}")
prism.stop_running_measure("srpl")
prism.close()
Coordinate Transformation
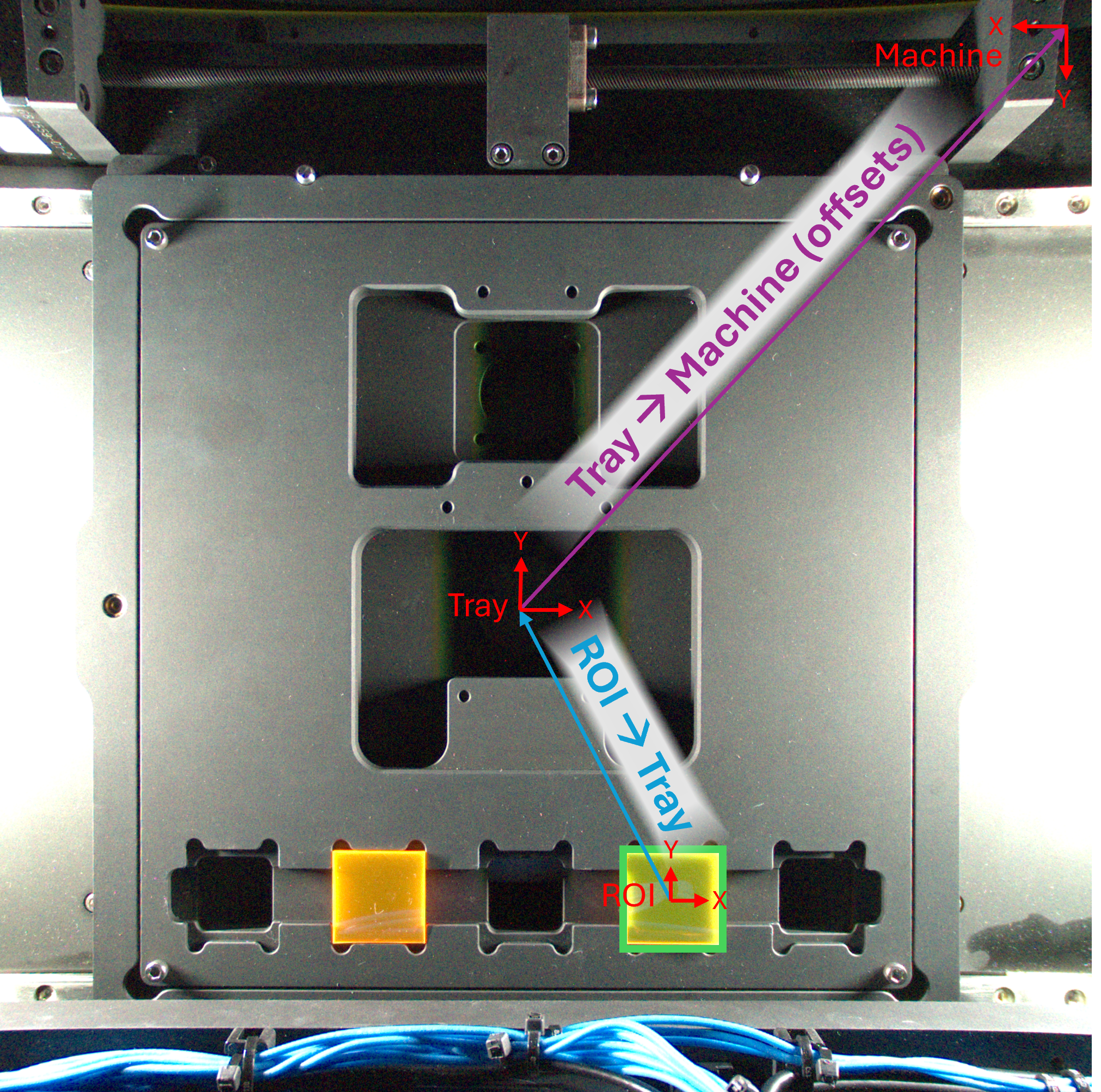
Fig. 1:Coordinate System Diagram
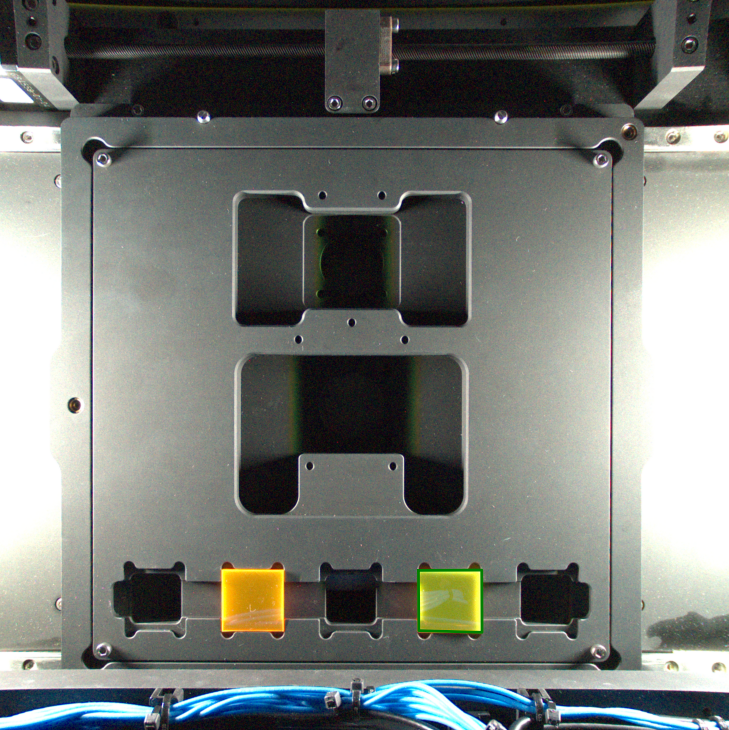
Fig. 2: ROI Example
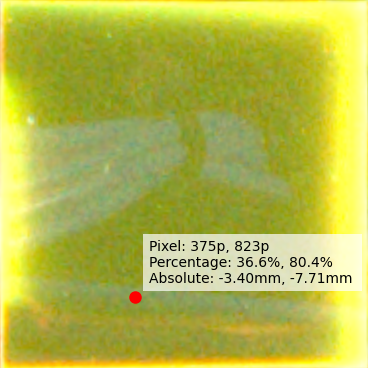
Fig. 3: Coordinate Example
"""
This example demonstrates how to transform coordinates from the ROI
coordinate system to the machine coordinate system. The general flow
is as follows:
1. Capture an image of the bed.
2. Identify the ROI in the image
3. Use relative location on the ROI to calculate ROI coordinates in mm
4. Use knowledge of ROI physical dimensions in tray coordinates to convert from ROI to tray
coordinates.
5. Use offsets to convert to machine coordinates.
"""
from prismapi import Prism
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from typing import Tuple, Dict
from getpass import getuser
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from os.path import isfile
def transform_coordinates(
roi_coord: Tuple[float, float],
roi_origin: Tuple[float, float],
offset: Tuple[float, float],
) -> Tuple[float, float]:
"""
Example helper function to transform from ROI coordinates to machine coordinates. See figure
'Coordinate Systems' in the documentation."""
return (
-roi_coord[0] - roi_origin[0] + offset[0],
-roi_coord[1] - roi_origin[1] + offset[1],
)
def get_offsets(settings_path: str = None) -> Dict[str, Tuple[float, float]]:
"""
Example helper function to get the offsets for each measurement type from the settings file.
"""
if settings_path is None:
user = getuser()
settings_path = f"C:\\Users\\{user}\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\prism_settings.json"
if not isfile(settings_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Settings file not found at {settings_path}")
with open(settings_path, "r") as f:
settings = json.load(f)
try:
return settings["settings"]["advancedKeyPoses"]["hardwareOffsets"]
except KeyError:
raise KeyError("Could not find hardware offsets in settings file.")
# Initialize the Prism interface
prism = Prism()
###############################################
### Capture bed image #########################
###############################################
# Move bed to imaging position
prism.move(106, 418)
# Turn on camera light
prism.set_parameter("camera_led_color", 100)
# Capture a bed camera image
image = prism.image_bed()
###############################################
###############################################
### Identify ROI coordinates ##################
###############################################
# Manually setting coordinates for simulator image
# ** Replace with pattern recognition of your own method **
fiducial_points = [
(1238, 1686),
(1425, 1685),
(1426, 1869),
(1239, 1864),
]
###############################################
###############################################
### Display captured image with ROI ###########
###############################################
# Extract x and y coordinates from fiducial points
x_coords = [point[0] for point in fiducial_points]
y_coords = [point[1] for point in fiducial_points]
# Create figure and axis
plt.figure()
# Plot rectangle using the fiducial points
plt.imshow(image)
plt.plot(x_coords + [x_coords[0]], y_coords + [y_coords[0]], "g-", linewidth=2)
plt.title("Bed Camera Image with ROI")
plt.axis("off")
plt.show() # Figure 2
###############################################
###############################################
### Remap ROI to 1024x1024 image ##############
###############################################
result_dimen = (1024, 1024)
# Calculate the dimensions of the ROI
roi_width = max(x_coords) - min(x_coords)
roi_height = max(y_coords) - min(y_coords)
# Create source points array from fiducial points
src_points = np.array(fiducial_points, dtype=np.float32)
# Create destination points for 1024x1024 image
dst_points = np.array(
[
[0, 0],
[result_dimen[0], 0],
[result_dimen[0], result_dimen[1]],
[0, result_dimen[1]],
],
dtype=np.float32,
)
# Calculate perspective transform matrix
transform_matrix = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src_points, dst_points)
# Apply perspective transform to original image
sample_image = cv2.warpPerspective(image, transform_matrix, result_dimen)
###############################################
###############################################
### Calculate example point coordinates #######
###############################################
# Manually choose point in pixels - replace with your own application logic
x_pixel, y_pixel = 375, 823
# Calculate percentages (origin at center)
x_pct = x_pixel / result_dimen[0] * 100
y_pct = y_pixel / result_dimen[1] * 100
# Calculate mm coordinates (25.4mm x 25.4mm with center origin)
x_mm = x_pct / 100 * 25.4 - 12.7
y_mm = 12.7 - y_pct / 100 * 25.4 # flip y axis - pixels are positive going down
###############################################
################################################
### Display example point and coordinates ######
################################################
# Create label with all coordinate representations
label = f"Pixel: {x_pixel}p, {y_pixel}p\nPercentage: {x_pct:.1f}%, {y_pct:.1f}%\nAbsolute: {x_mm:.2f}mm, {y_mm:.2f}mm "
plt.plot(x_pixel, y_pixel, "ro", markersize=8)
plt.annotate(
label,
(x_pixel, y_pixel),
xytext=(10, 10),
textcoords="offset points",
bbox=dict(facecolor="white", edgecolor="none", alpha=0.7),
)
plt.title("Cropped/Remapped Image with desired coordinate")
plt.imshow(sample_image)
plt.axis("off")
plt.show() # Figure 3
###############################################
###############################################
### Convert to machine coordinates (SRPL) #####
###############################################
try:
offsets = get_offsets()
except FileNotFoundError or KeyError:
print("Failed to get offsets from settings file. Using mock offsets.")
offsets = {"srpl": (106, 287.5)}
machine_coords = transform_coordinates(
(x_mm, y_mm),
(40, -80), # From knowledge of ROI physical dimensions in tray coordinates
offsets["srpl"],
)
print(f"Machine coordinates: {machine_coords}")
prism.move(*machine_coords)
###############################################
prism.close()